High performance multi-physics simulations with FEniCS/DOLFIN
eCSE03-10Key Personnel
PI/Co-I: Dr. Garth N. Wells - University of Cambridge
Technical: Dr. Chris Richardson - University of Cambridge
Relevant Documents
eCSE Technical Report: High performance multi-physics simulations with FEniCS/DOLFIN
Project summary
High performance computing (HPC) depends on being able to run code in parallel, on many compute nodes at the same time. We would like to solve mathematical equations for different kinds of problem, such as heat flow, elasticity, fluid flow or electrodynamics, on large HPC machines. Some equations are simple, but some equations have dependencies on each other. For example, in fluid flow, we can consider the conservation of mass as one equation and the conservation of momentum as another equation. Both equations involve the fluid flow velocity. Solving these coupled equations on HPC systems can be very challenging. At large scale, we have to use iterative methods to solve the equations, and the memory use on HPC machines can quickly take over the whole memory, unless special precautions are taken to optimise the way we use it.
In this project, we developed new functionality in the open source FEniCS/DOLFIN libraries that optimise the memory usage for coupled problems, by re-using the same memory block twice, and avoiding copying during the solve phase. We can now solve larger coupled problems on HPC machines than was previously possible with DOLFIN.
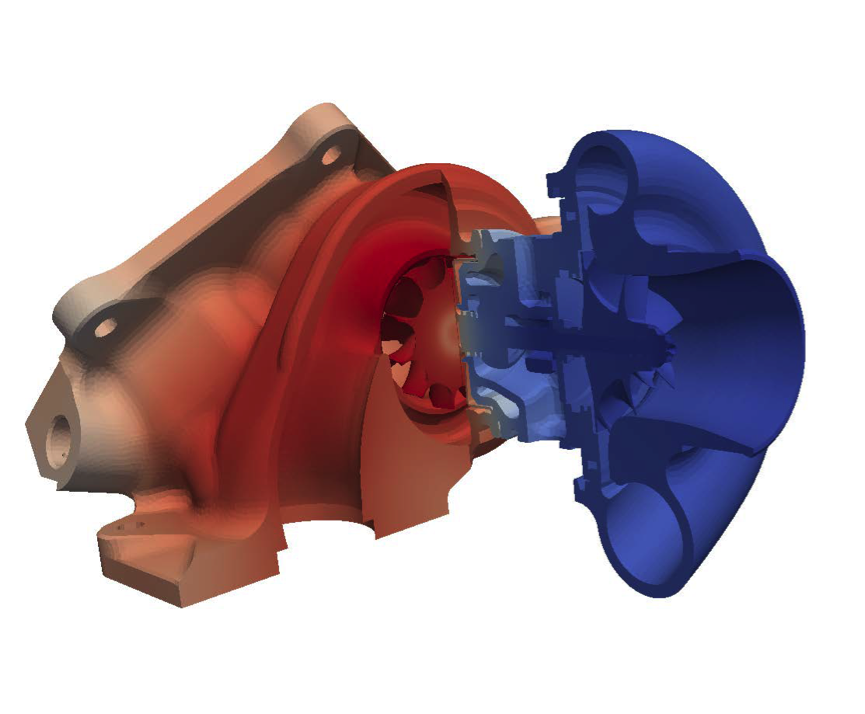
When solving an engineering problem, the task is described on a mesh which is subdivided into "cells". In a recent project, we have now targeted problems on meshes with tens of millions to billions of cells. For many industrial problems, it is increasingly necessary to target such large meshes. Complex engines, aerospace parts and high resolution climate models all need such huge meshes. An example is shown below, from an industrial research project, which was made possible by our software developments in this project. The largest mesh we have solved on to date has 3.84 billion cells.
Summary of the software
The FEniCS course code is available at: https://bitbucket.org/fenics-project under open source licences. Installation instructions can be found at: http://fenicsproject.org. Release versions of FEniCS are available on ARCHER with the "module load fenics" command. The enhancements from this eCSE project are incorporated in the FEniCS development repositories, and will be included in a future release of FEniCS and made available on ARCHER as a module.






